Firs ( Abies ) are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family Pinaceae .
All fir species are evergreen deep-rooted trees with a straight, columnar trunk.
The conical crown is formed from regular tiers of relatively short, horizontal branches.
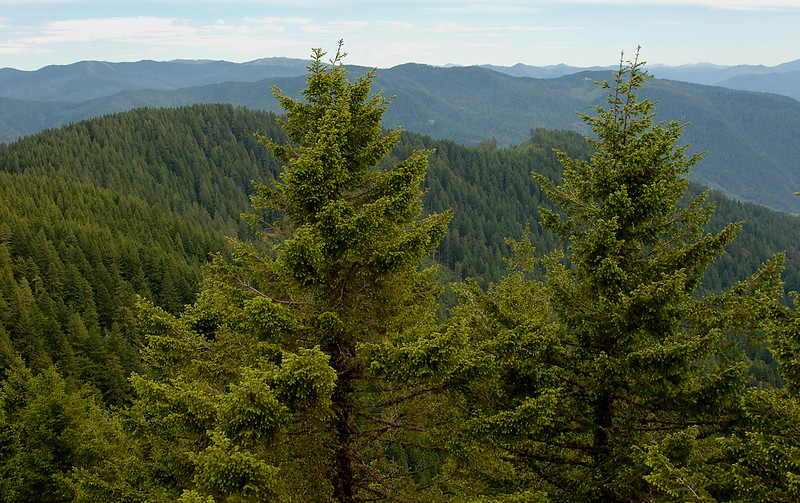

A few species remain relatively small with a growth height of 20 meters, but most species are dominant forest trees in their habitat and then often belong to the largest forest tree species (the European silver fir is considered the largest tree on the continent).
Most fir trees grow to heights of between 40 and 70 meters, but some American species are also known to grow to 90 meters ( Abies grandis , Abies procera ).
The genus name is derived from the Latin "to rise" in reference to the height of its species.
They are large trees, reaching heights of 10–80 metres tall with trunk diameters of 0.5–4 m when mature.
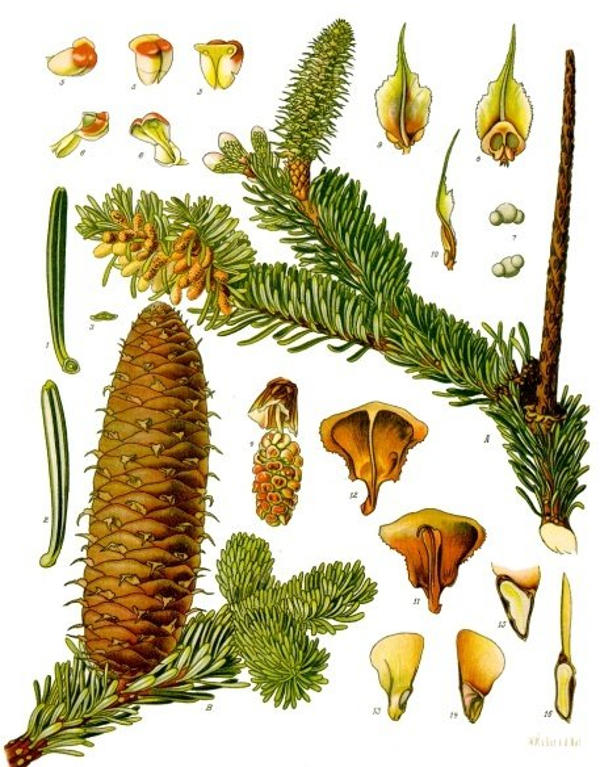

the European silver fir or silver fir
Firs can be distinguished from other members of the pine family by the way in which their needle-like leaves are attached singly to the branches with a base resembling a suction cup , and by their cones , which, like those of true cedars, stand upright on the branches like candles and disintegrate at maturity.
The needle-shaped leaves are flat and easily pliable.
The leaves have two whitish lines on the bottom, each of which is formed by wax -covered stomatal bands.
Fir trees are important trees for landscaping and garden design.
Many are decorative garden trees, which produce brightly coloured cones even when very young, still only 1–2 m tall.
source of information wikipedia.org