The oaks (Quercus) are a genus of plants in the beech family (Fagaceae).
Oak species are deciduous or evergreen trees, more rarely shrubs.
Quercus is the most important genus of deciduous trees in the northern hemisphere.
Includes deciduous and evergreen species extending from cool temperate to tropical latitudes in the Americas, Asia, Europe, and North Africa.
The genus Quercus includes between 200 and 600 species (variable figure according to the authors, given the large number of hybrids) located mainly in the northern hemisphere, of which about twenty species grow spontaneously in Europe.
Oaks are keystone species in a wide range of habitats from Mediterranean semi-desert to subtropical rainforest.
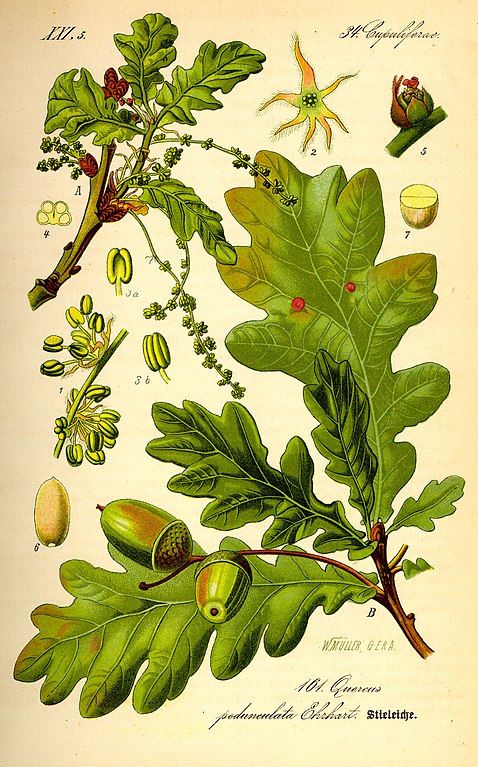

Quercus robur, the pedunculate oak
Depending on the location and species, an oak tree can reach a height of around 30 to 40 meters and in some cases over 1000 years.
An adult oak can daily pump up to 200 liters of water at a height of 30 m.
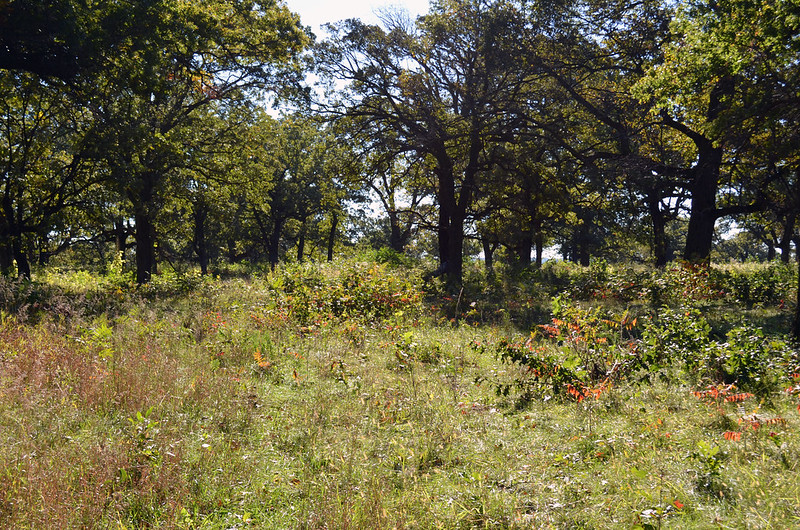

Oaks are enjoying a place in full sun in an open place, they colonize extremely diversified environments.
Unless it grows in the middle of a clearing, due to slow growth, in primary subnatural mixed (hardwood-softwood) mixed forest, it takes 100 to 150 years to reach the canopy, but this slow allows the oak to produce a dense and hard wood, appreciated for many uses.
If left to live, the oak easily exceeds 500 years, and up to more than 1000 years, exceptionally.
Where it is naturally present in its area of distribution, the oak shelters hundreds of other species (in particular after its life in its dead wood); to the point that some ecologists call it a biodiversity hotspot.
An oak forest is an oak grove. Oak often forms mixed forests in association with other hardwoods.
As a general rule, it is in the temperate regions that the areas of distribution occupy the largest surfaces, on the scale of the continents.
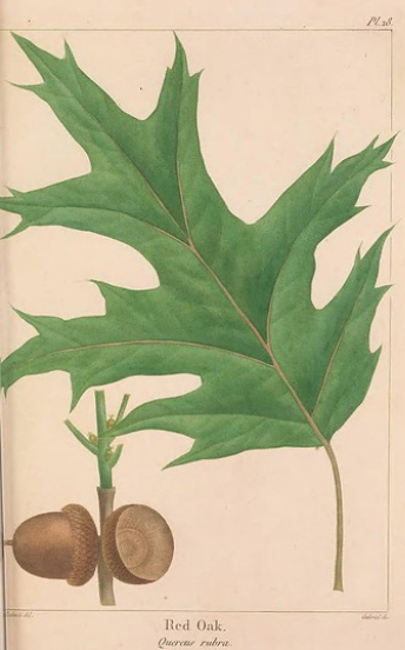

Quercus rubra, the red oak
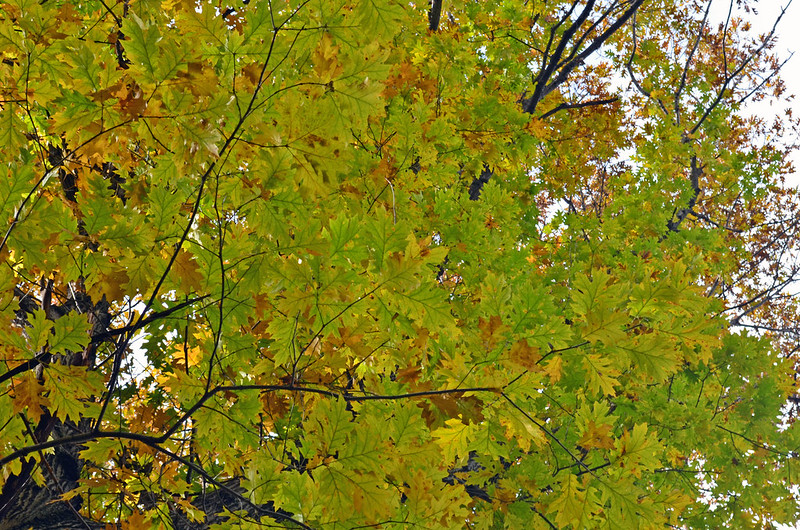

Botanists distinguish two main categories of oaks: deciduous oaks whose foliage falls in autumn, sometimes in spring (red oak, Turkey oak, pubescent oak, Tauzin oak and sessile oak); sclerophyllous oaks whose leaves are evergreen: trees growing mainly on the Mediterranean shores (holm oak, kermes oak and cork oak) as well as in subtropical and tropical zones in America and Asia.
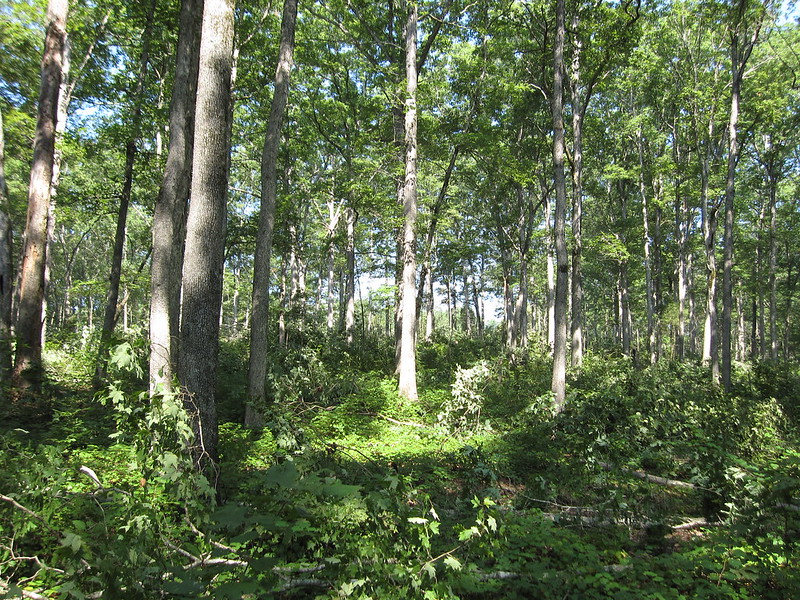

In Europe, oak is widely used and cultivated for its wood, cork, bark and acorns.
Oaks are hardwood trees. Oak wood has a density between 0.75 and 0.85 g/cm3. It is a very resistant and very hard material.
Its resistance to insects and fungi is very important thanks to its high tannin content.

The wood of the pedunculate oak and the sessile oak (Quercus petraea) was used in Europe for shipbuilding until the 19th century and were the main species of wood used in the construction of the wooden frames of buildings in Europe. Today oak wood is still commonly used in joinery, flooring, and veneer production.
source of information wikipedia.org